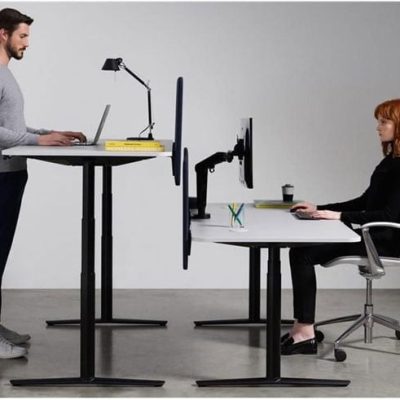
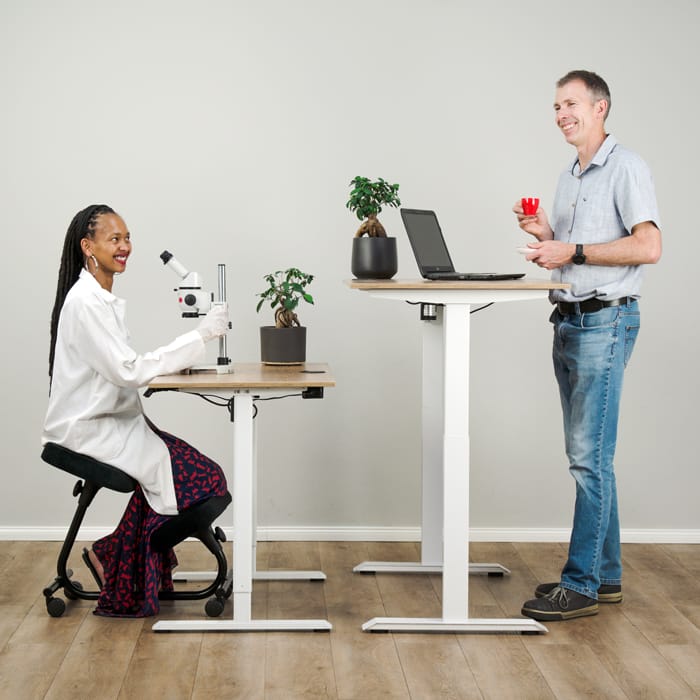
An ergonomic workplace is crucial for the health and well-being of all employees. Aches, wrist injuries, and other discomforts can lead to decreased employee morale, increased absenteeism, and overall diminished productivity. Implementing effective ergonomic practices in the workplace involves more than simply rearranging furniture or investing in an expensive office chair. This article will serve as a comprehensive guide on enhancing office ergonomics to create a healthier and more productive work environment, potentially reducing the risk of mental health challenges in the workplace. Additionally, I will offer practical tips and identify possible risk factors.
According to a report published by MedicalBrief, low back pain is a leading cause of disability‚ affecting an estimated 540 million people worldwide at any one time.
Evidence suggests that low back pain should be managed in primary care‚ with the first line of treatment being education and advice to keep people active and at work. The dangers of sitting: why sitting is the new smoking.
Ergonomics in the Workplace:
How to correctly adjust the height of your OFFICE CHAIR, DESK and MONITOR
Watch the short video!
Alternatively, continue reading for a more detailed analysis.
1. Improving ergonomics in the workplace – Adjusting your OFFICE CHAIR
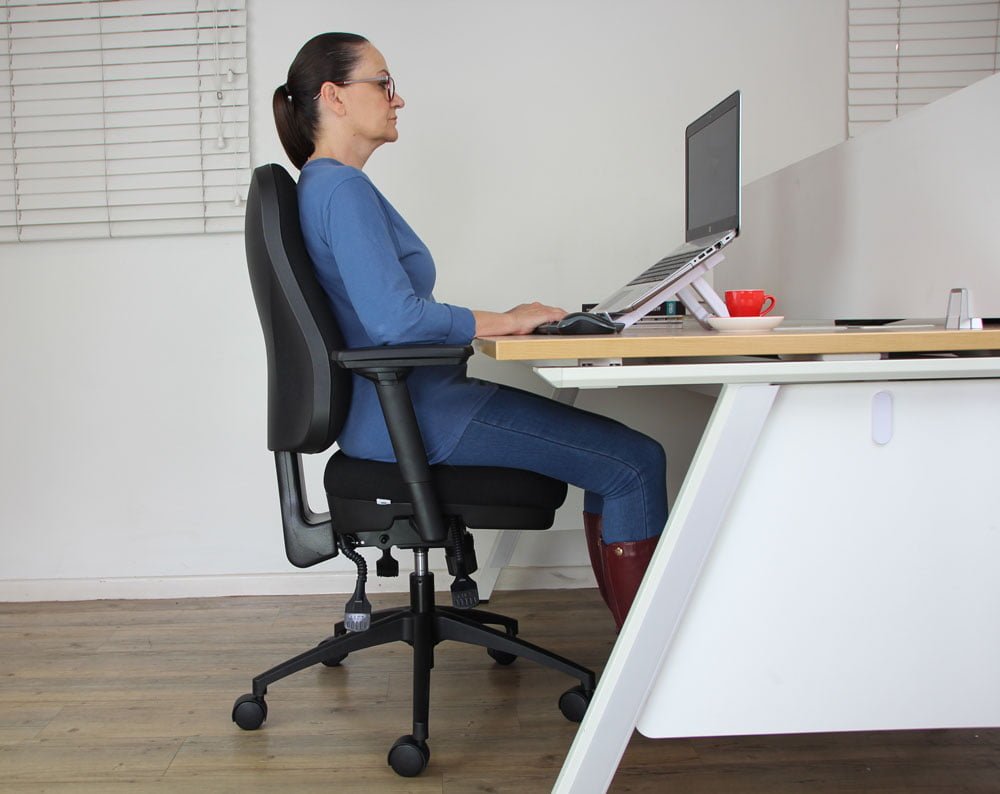

For office workers, an ergonomic chair is the most essential item in the workplace, and sitting on the wrong chair can be detrimental to your long-term health. For anyone working in a call center or control room, an ergonomic chair should be their number 1 priority.
Adjusting your chair to the correct position is critical to avoid common posture-related hazards, and is the first step to improving the overall ergonomic setup in your place of work. What does a cheap office chair REALLY cost me?
The importance of your office chair...
1.1 Adjusting your chair
a. Seat height
- Move the chair AWAY from your desk.
- Now sit on your chair making sure your back is against the backrest of the chair.
- Adjust the seat height. The correct chair height is when both your feet (with shoes), are flat on the floor and your knees are slightly lower than the level of your hips.
- By sitting with your knees below the level of your hips you reduce the rotation of the pelvis which in turn reduces the pressure in the lumbar discs. What happens when you sit?
- What is the correct height for my chair, desk and monitor?
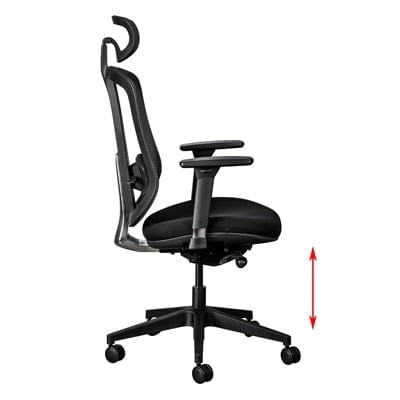


b. Seat depth
If your office chair has a seat depth adjustment feature, slide the seat pan forward or backward until there is a 2-3 finger gap between the back of your knees and the front edge of the seat. Your back should be resting comfortably against the chair backrest.
If a number of people are going to use the same office chair throughout the day, a chair with a seat slider allows each person to change the seat depth to suit their leg length, thereby maintaining a correct ergonomic seated posture. These office chairs have a seat slider.
c. Backrest height and lumbar support
- If your chair has a height adjustable backrest, move it up or down so that the lumbar area fits snugly into your lower back.
- Adjust the lumbar support (if available), so that it fits comfortably into your lower back.
- Back support for an office chair – why it’s important
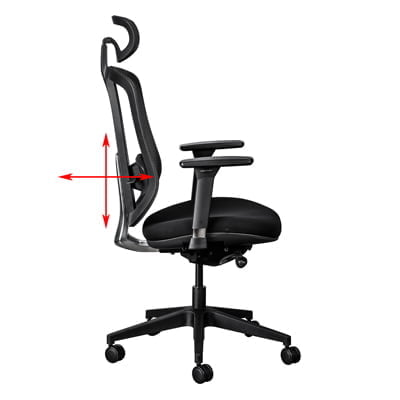
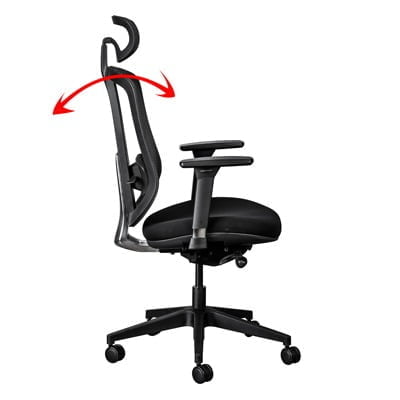


d. Backrest angle & Tension
- The backrest can usually be locked in an upright position or at various angles. We recommend that you keep the backrest in a free-float position to promote dynamic sitting. By doing so, the muscles in your lower back and core are stimulated, thereby improving blood flow and reducing muscle fatigue.
- If available, adjust the tension of the backrest movement to suit your body weight. Some chairs have a self-tensioning feature built into the mechanism which will automatically tension the backrest according to your body weight.
- Tilt Tension Troubles: How to Get It Just Right
e. Armrests
- Adjust the height of the chair armrests. Your elbows should be bent at about 900 with your forearms parallel to the floor.
- Change the width of the armrests (if available), so that your arms are close to your body.
- Move as close to the desk as possible.
- Adjust each arm capping (if available), into a comfortable position.
- What is the difference between office chair armrests.


f. Headrest (optional)
If your chair has a headrest, move it vertically and rotate it so that it supports your neck and the lower part of your head.
2. Improving ergonomics in the workplace – Adjusting your DESK
Your desk is the second most important piece of equipment in your office and plays a major role in the overall ergonomic setup. With so much emphasis on the correct office chair setup, people often neglect the proper ergonomic setup of their desk and other equipment in their place of work. The incorrect configuration of your desk, computer and ancillary equipment, can contribute to stress at work, poor posture and other long-term health issues.
Once you have setup your chair, move it towards your desk. If you are working on a computer, your desk should be at the same height as the top of armrest on your chair.
The desk is at the correct height when your elbows are bent at approximately 900 and your forearms are resting on the surface of the desk. Your forearms will now be parallel to the floor.
If your hands are on the surface of the desk and forearms are NOT parallel to the floor, then your elbows cannot be at 900. If your elbows are bent at less than 900, then the desk is too high. Conversely, if your elbows are bent at more than 900, your desk is too low. What is the correct height for my desk, computer monitor and office chair?
Left image:
Desk is too high and the angle of the elbows is less than 900. Forearms are not parallel to the floor.

Right image:
Desk is too low and angle of the elbows is greater than 900. The hunched back typically results in pain in the back and shoulders.
IMPORTANT!
- If the desk is too high, raise the height of your chair until your elbows are at 900 and your forearms are resting on the surface of the desk, and are parallel to the floor. This will result in your feet no longer being flat on the floor, so use a footrest, books, etc, to support your feet.
- If the desk is too low, raise the height of the desk. Place blocks or spacers under the desk legs until your elbows are at 900 and your forearms are resting on the surface of the desk, and are parallel to the floor. DO NOT lower the height of your chair. If you do, the chair will no longer be adjusted correctly!

2.1 Height adjustable desks can improve ergonomics in the workplace
In conjunction with your chair, for the best ergonomic practices at work use a height adjustable standing desk.
Whether gas, manually or electrically actuated, these desks allow you to adjust the height of your work surface to an ergonomically correct position. Most importantly, they also enable you to alternate between sitting and standing while you work. The 7 Advantages of a Standing Desk

Remaining in one position for long periods, be it sitting or standing, will have a negative effect on your overall health.
2.1.1 Useful tips when using a height adjustable desk
- Use anti-fatigue mats to reduce strain in your legs.
- Wear supportive footwear.
- Shift positions frequently. Rest one foot on a footrest and regularly alternate with the other foot.
2.1.2 Advantages of alternating between sitting and standing while you work
- Stimulates circulation.
- It keeps your intervertebral discs in a better shape.
- Reduces possibility of varicose veins.
- Improves concentration.
2.1.3 Negative effects of sitting too long
- Muscle fatigue which results in bad posture.
- Poor blood circulation and concentration.
- Muscle tension and pain in the neck, back and shoulders.
2.1.4 Negative effects of standing too long
- Fatigue in your legs.
- Inflammation of veins and possible varicose veins
2.2. The area around your desk
The way you arrange your keyboard, monitor, mouse and other ancillary equipment on your desk, can have a huge impact on your posture and wellbeing. Even with the correct desk and chair setup, you may still experience discomfort in the neck and shoulders. This is often as a result of excessive leaning, twisting or over-reaching for items on your desk.
2.2.1 Working Zones can improve ergonomics in the workplace
Your frequently used equipment and documents should be placed within your Inner Zone (regular and occasional work area). Your regular work area is the most important area as it is the closest to your body and within easy reach. This is where the keyboard and mouse should be placed.

Avoid ergonomic hazards in the workplace like neck and shoulder pain by creating Inner and Outer zone working areas on your desk.
- If you constantly use your phone, place it in the Regular work area or use a headset. Avoid cradling the phone between your neck and shoulder.
- Items that are not used regularly should be placed in the occasional work area. These items should still be within reach when your arm is extended but without having to lean over.
- To prevent over reaching and stretching, avoid placing items that you use often in the Outer Zone (non-working area).
- If you use a document holder, place it between your keyboard and monitor. The ideal position is directly below your screen to prevent unnecessary bending of your neck.
3. Improving ergonomics in the workplace – using your KEYBOARD, MOUSE and MONITOR

3.1 Keyboard
The keyboard should be flat on the desk, although some people prefer a slightly angled keyboard. Try different angles to find the most comfortable position for you. Ensure that your wrists remain in a neutral position to reduce fatigue and potential injury. Move the keyboard close to the front of the desk.
Do not place documents between the keyboard and the front edge of the desk as this increases the reach distance to the keyboard.
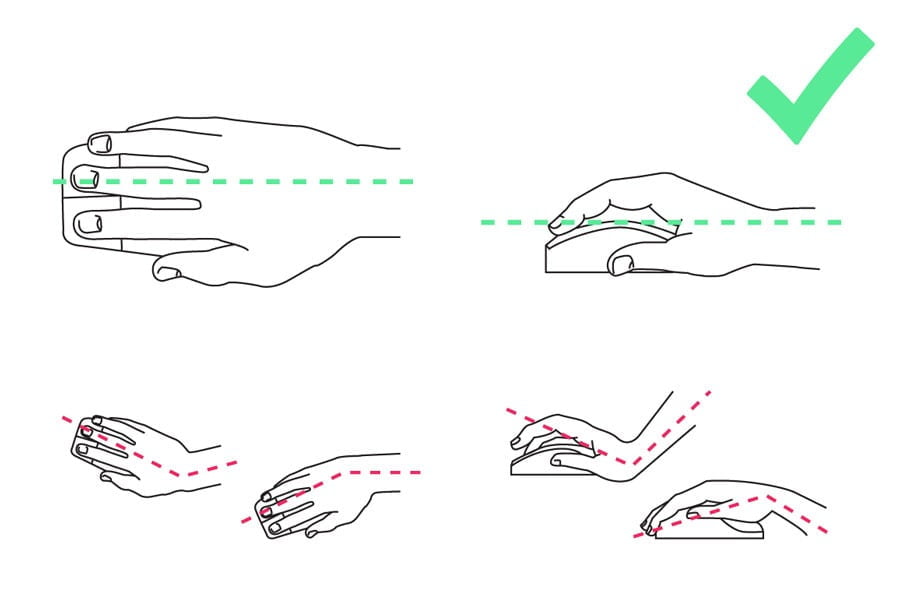
3.2 Mouse
Place your mouse as close as possible to the keyboard to minimise forward or side reach. Remember to maintain a 900 elbow angle. Maintain a straight wrist position when you are using the mouse.
The fine movement of the hand, fingers and thumb repeated for hours on end can cause repetitive strain injury (RSI). A mouse that fits your hand poorly can cause thumb tendinitis.
3.3. Monitor
3.3.1 Single monitor setup
- Sit upright and centre the monitor so that it is directly in front of you.
- Adjust the monitor height until the top of the monitor is at or just slightly below the level of your eyes. If you don’t have a monitor arm to adjust the height of the monitor, use books to raise it’s height.
- Your eyes should look slightly downward when viewing the middle of the screen.
- Position the monitor approximately one arm’s length away from you (50-60cm). Sitting too close or too far from the monitor can cause eye strain.
- Based on your eyesight, adjust the monitor by slowly moving it towards you or further away until you can view the text comfortably. Larger screens require a greater viewing distance.
- Tilt your monitor slightly upward to enable easy viewing and reduce glare. Tilting the monitor too far back may cause glare from overhead lighting.
- Have regular eye breaks. Look 20 meters away for 20 seconds every 20 minute. This will allow the muscles in your eyes to relax.
3.3.2 Dual monitor setup
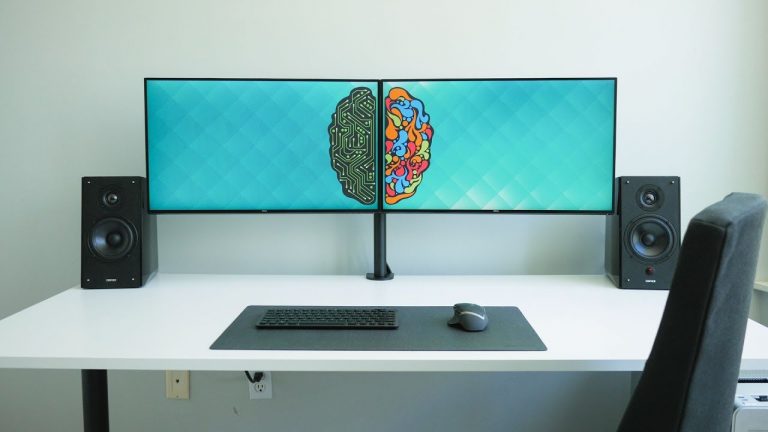

Your primary monitor (the one you use most frequently), should be centered directly in front of you, and the secondary monitor should be placed slightly off centre and at the same height and distance as the primary monitor. If both monitors are used equally, place them side by side at the same height with the inner edges touching.

4. Using a laptop and improving ergonomics in the workplace
Improving ergonomics in the workplace would not be complete without a discussion on laptops. Laptops were originally designed for short-term and mobile use but are now commonly used as a primary computer.

If you use a laptop continuously, you can reduce the stress in your neck and shoulders by:
- Using a laptop stand or books to elevate the screen to eye level.
- Alternatively use an external monitor with a separate keyboard and mouse.
- Due to the size of laptop screens, you may have to adjust the font size.
5. Health risks
5.1 Other factors to consider when setting up your monitor
- Place the monitor parallel to the window and not in front of windows.
- Place the monitor in a location that eliminates glare on the screen. If you can’t avoid the glare then invest in an anti-glare screen.
- Reading glasses work best for shorter distances and may not be the best for regular computer use. If you experience eye strain, blurred vision, tired eyes, or difficulty focusing on the screen, then chances are you may need computer glasses.
- Don’t place the monitor directly under overhead lighting but rather in between overhead light panels.
- Avoid having a window directly behind the monitor to prevent glare from the window.
6. Conclusion
Recognising the importance of ergonomics in the workplace is the first step in creating a beneficial environment for YOUR health and wellbeing.
Best ergonomic practices always begin with your chair followed by your desk. Your chair is the single most important piece of equipment in your office. Adjust it correctly!
For greater overall comfort, adjust the ambient temperature to about 250C. Lastly, to enhance the mood in your office, add some of your own stuff like photos, plants and music, as it creates a sense of identity!
Contact us for more information.
By the same author:

Why a fully adjustable office chair is important
We are all different, so when you buy a new office chair, look for one that has all the adjustability features.

What are the health benefits of a document holder?
One of the best ergonomic accessories you can get is a document holder.

Unveiling the True Cost of Ergonomic Office Chairs: Are they Worth the Investment?
Although the upfront cost of ergonomic office chairs may seem high, over their lifespan they are a low-cost and smart investment.




