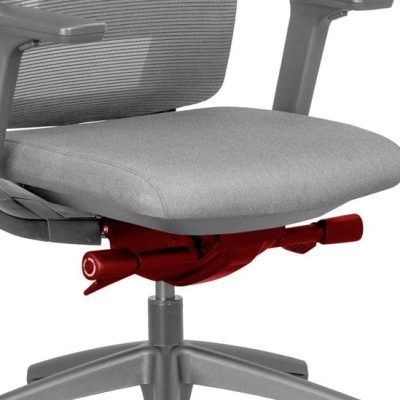
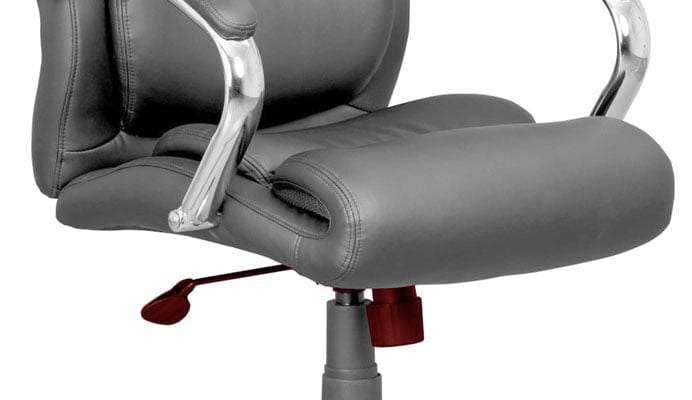
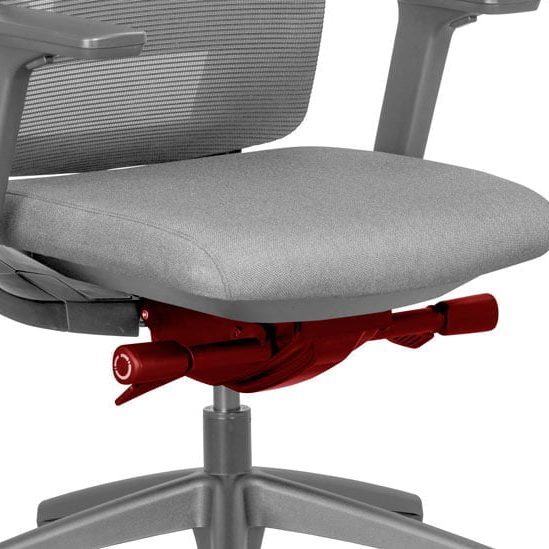
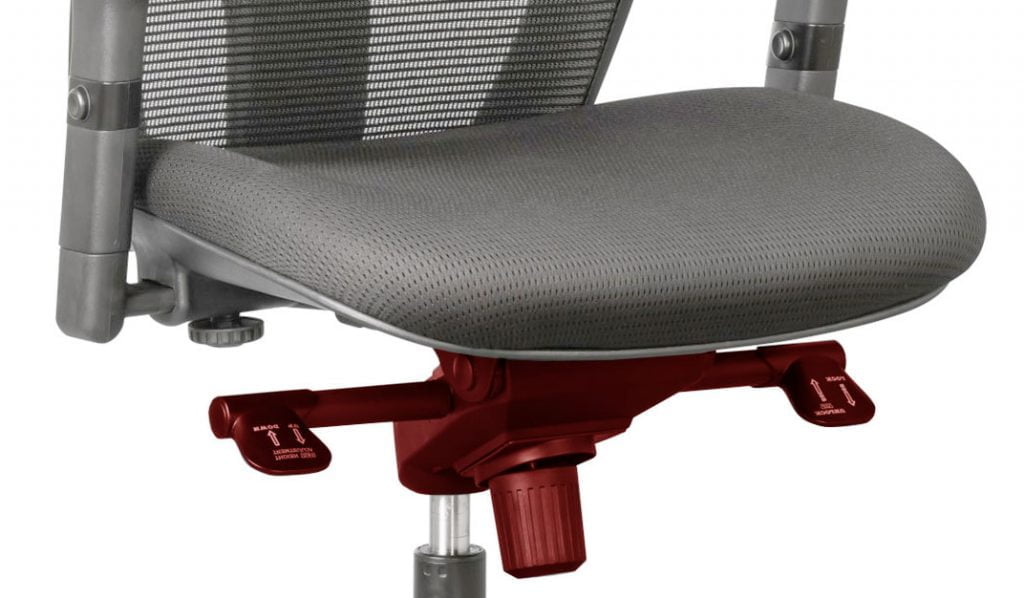
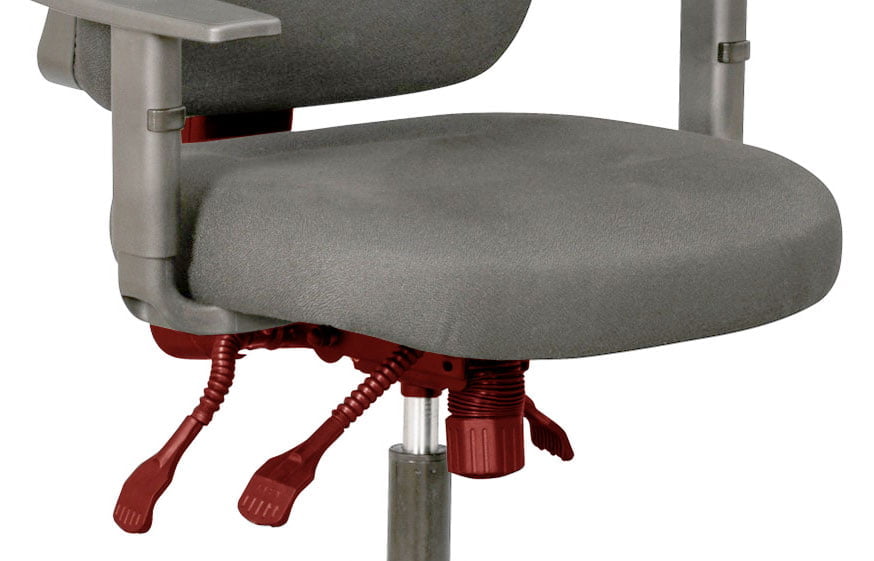
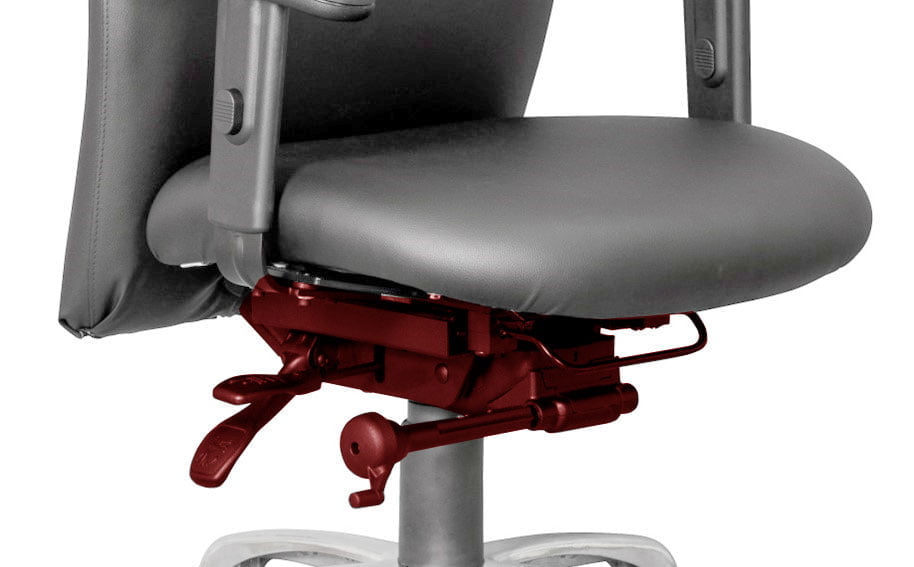
Located underneath the seat of an office chair is the chair mechanism. This is a mechanical component that enables you to make specific adjustments to the seat and backrest of the chair, for example the seat height and angle of the backrest. The mechanism allows you to personalise your seat position for optimal comfort and support. Why a fully adjustable office chair is important. There are different types of office chair mechanisms available, but how do they work and what is the difference between them?

The mechanism is the “heart” of an office chair.
Selecting the right one can make all the difference for your long-term comfort. Latest Trends in Selecting a Comfortable Office Chair.
Most types of office chair mechanisms have multiple adjustment levers and knobs which control the various movements, namely, seat height, backrest tilt, seat tilt, tilt tension, and seat depth. The Centripetal Spring Arm Chair of 1849 was the first to include a mechanism – history of office chairs.
Let’s take a look at all the major office chair mechanism types and discuss their differences and how they work.
Before doing so, it is important to understand how the chair mechanism influences static and dynamic sitting.
Static and Dynamic Sitting
a. Static Seating
Ergonomic office chairs should allow both “static” and “dynamic” sitting. The correct static seated position is shown below:
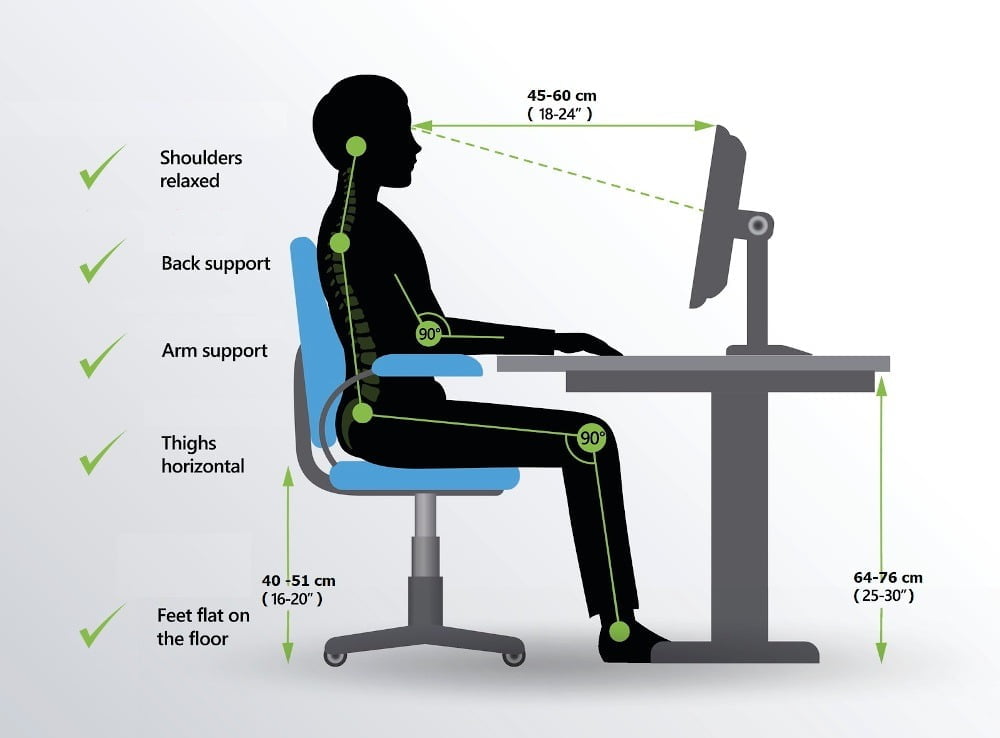
The checklist for a correct static seating posture is where your:
- Feet are resting flat on the floor or on a footrest.
- Knees are slightly below the level of your hips so that the angle between you back and thighs is between 90 and 100 degrees. Your knees should be bent at approximately 90 degrees.
- Arms are well supported by the armrests with your elbows bent at about 90 degrees.
- Hands and wrists are at the same height or slightly higher than the top of the desk.
- Back is well supported by the chair backrest and lumbar support.
- Shoulders and neck are in a relaxed position with your head straight.
- The distance from your eyes to the monitor should be approximately arms-length, with the upper edge of the screen at about eye level.
Sitting statically in the above posture minimises the strain on your body. However, maintaining this posture for a long period is not possible. As you work, the continual inactivity (or static loading), of your core muscles causes them to get tired, and so you begin to slouch in your chair.
For optimum comfort, you should be able to continuously alternate between a static and dynamic seated posture, and the mechanism on your office chair should facilitate this.
If it doesn’t, consider replacing your chair!
b. Dynamic Seating
Dynamic sitting occurs in an office chair that is fitted with a mechanism that allows the backrest and seat to move relative to each other. This movement automatically stimulates, or activates various muscles in your lower back, core and legs. As a result, the blood-flow through these muscles increases, which prevents them getting tired. Dynamic Sitting has long been acknowledged as the global benchmark for ergonomic comfort.
An office chair fitted with a mechanism that facilitates dynamic sitting, is more comfortable.
Categories of Office Chair Mechanisms
There are 7 major categories of mechanisms available for office chairs, all of which will allow you to adjust the height of the seat. With the exception of the swivel-only mechanism, they all provide additional functionality. What is the difference between the various types of office chair mechanisms and how do they work?
Below we describe each category and give the mechanism a Dynamic Rating Score based on its ability to facilitate dynamic sitting.
1. Swivel-Only Mechanism
The Swivel-Only Mechanism is typically found on a sit/stand stool where you continuously alternate between sitting and standing. Good examples are laboratories, factories and salons.
2. Swivel & Tilt Office Chair Mechanism
This mechanism works on all office chairs where the seat and backrest are one continuous piece. In these chairs, the seat and backrest cannot be separately adjusted and will always move together in the same direction.
The pivot point for these mechanisms is usually in the centre of the seat. This means that when you tilt backwards in the chair, the front edge of the seat will have a tendency to lift your feet upwards, and so increase the pressure on the underside of your thighs.
3. Frontal Pivot Mechanism


A Frontal Pivot or Knee-Tilt office chair mechanism, is exactly like a normal Swivel & Tilt (#2 above), except that its pivot point in not in the centre of the seat, but closer to the front of the chair. This results in a wide-angle tilt that keeps the front of the seat relatively level. Unlike a normal swivel & tilt mechanism, the frontal pivot does not result in an increase in pressure on the underside of your thighs when the chair tilts backwards.
The pivot point for these mechanisms is usually in the centre of the seat. This means that when you tilt backwards in the chair, the front edge of the seat will have a tendency to lift your feet upwards, and so increase the pressure on the underside of your thighs.
4. Permanent Contact Mechanism

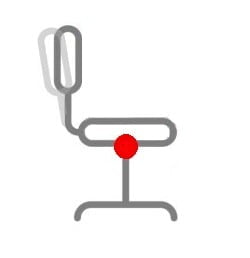
A Permanent Contact or Back-Rake Mechanism, allows you to adjust the angle of the backrest. The angle of the seat cannot be changed and remains fixed in a horizontal position. Office chairs that are fitted with a Permanent Contact mechanism are ideally suited for occasional use and are not recommended for intensive use.
A Permanent Contact mechanism allows you to lock the backrest into any desired position, often referred to as infinite lock. Typically, the height of the backrest can also be adjusted so that you can align it with the natural curvature of your spine.
5. Synchronous (Synchro) Mechanism
Synchro mechanisms have a mechanical tilt that moves both the chair’s backrest and seat together in a fixed ratio. All synchro mechanisms ensure that the movement of the backrest is greater than the movement of the seat. Typically synchro mechanisms have a 2:1 ratio i.e. the backrest moves 2 degrees for every 1 degree of movement in the seat.
The seat and backrest can be locked into a number of static positions. If the mechanism is unlocked, it will be in a free-float position. In this position, the chair is dynamic and the backrest gives continual back support by moving with you.
A synchro mechanism enables dynamic sitting and is therefore recommended for professional intensive use.
6. Synchronous Frontal Pivot Office Chair Mechanism
Synchro mechanisms have a mechanical tilt that moves both the chair’s backrest and seat together in a fixed ratio. All synchro mechanisms ensure that the movement of the backrest is greater than the movement of the seat. Typically synchro mechanisms have a 2:1 ratio i.e. the backrest moves 2 degrees for every 1 degree of movement in the seat.
7. Free-Float Mechanism
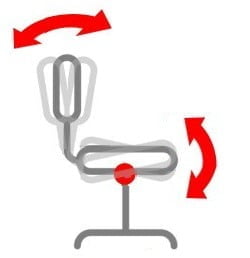
A Free-Float or Multi-function mechanism allows you to independently adjust the backrest and seat of the chair. This enables you to customise the exact angle of the seat and backrest to create your optimal sitting posture.
All orthopedic office chairs use a Free-Float mechanism.
The seat angle can also be set at a negative tilt (forward sloping), to create an ‘open’ angle at the hips of approximately 100 degrees, resulting in the Perfect Ergonomic Office Setup. According to Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), a forward sloping seat helps increase blood flow to the lower extremities and at the same time reduces the pressure in the discs of the lower back. Why my back hurts when I sit?
In a static seating position you can lock the movement of both the seat and the backrest independently and in any position. In the free-float position, the chair is dynamic and the backrest provides continual back support by remaining in contact with your back and moving with you. Due to its highly advanced functionality, the free-float mechanism is suitable for professional and intensive use.
A Free-Float mechanism offers you the best orthopedic comfort and has the highest Dynamic Rating of all mechanisms.
Conclusion
Choosing the right office chair for your needs is critical for your long-term comfort and wellbeing at work. The type of mechanism fitted to the office chair plays a huge role in its overall comfort. A chair with a mechanism that has a “good” or “excellent” Dynamic Rating is essential if you spend many hours sitting at your workstation.
Related articles:
How do I choose the best office chair for me?
What influences the price of an office chair?
What is the difference between office chair armrests?
By the same author:

What Is An Ergonomic Chair And How Do I Select My Ideal Seat?
There are many options available, but what is an ergonomic office chair? What features must it have? How do you make the right choice?

Office Furniture Suppliers for Ergonomic Solutions
Choosing the right office furniture suppliers in South Africa is crucial for creating a productive, comfortable, and stylish workspace.

Home Office – how to select the best chair
Discover essential features to look for in a home office chair and learn how to create the perfect workspace that supports your body.